Heat Capacity of Calorimeter
T 2 T 1 is the temperature difference before and after heating or cooling K. The Parr 1108P Oxygen Bomb furnished with the calorimeter will safely burn samples liberating up to 8000 calories per charge using oxygen charging pressures up to 40 atm.

Basic Calorimeter For Measuring Heat Capacity Is A Foam Coffee Cup Calorimeter Heatcapacity Coffee Cups Heat Heat Transfer
After the reaction the final temperature is 328C.

. Table of Specific Heat Capacities. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is the most frequently used thermal analysis technique. A bomb calorimeter is used to measure heat flows for gases and high-temperature reactions.
The water increases in temperature by 10 degrees C. Specific heat capacity is the most useful quantity available from DSC because it is directly related to sample properties and. A Reliable Oxygen Bomb.
C is the specific heat of a material JgK. Clamp the thermometer into the smaller hole with the stirrer. Assuming that all the solutions have a density of 10 gcm3 and a specific heat capacity of 418 JCg calculate the enthalpy change for the neutralization of HCl by NaOH.
Both solutions were originally at 261C. Soc 1929 51 2738. In a coffee cup calorimeter the reaction takes place in the water while in a bomb calorimeter the reaction takes place in a sealed metal container which is placed in the water.
Q is the heat absorbed or released by a material J. To calculate the energy required to raise the temperature of any given substance heres what you require. The heat capacity of toluene from 14 deg K to 298 deg K.
If specific heat is expressed per mole of atoms for these substances none of the constant-volume values exceed to any large extent the theoretical. Therefore specific heat capacity c Qm Delta T. Heat loss by the fuel is equal to the heat gained by the water.
Science Chemistry QA Library In a coffee-cup calorimeter 1200 mL of 10 M NaOH and 1200 mL of 10 M HCl are mixed. In the 18th and 19th centuries scientists abandoned the idea of a physical caloric and instead understood. Say in a calorimeter a fixed amount of fuel is burned.
We will be measuring the change in temperature of the water in the calorimeter which lets us calculate the change in heat of the water in the calorimeter which we know to be equal and opposite to the change in heat of the sample. Heat capacity ratio of heat absorbed by a material to the temperature change. Heat flow is proportional to the heat difference of heat sink and holders.
In case the sample occurs endothermic or exothermic phenomena such as transition and reaction this endothermic or exothermic phenomena is compensated by heat sink. M is the mass of a material g. The only thing you need to remember is that you have to use consistent units for mass.
A calorimeter is an object used for calorimetry or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacityDifferential scanning calorimeters isothermal micro calorimeters titration calorimeters and accelerated rate calorimeters are among the most common types. A sealed immersion heater and a built-in heat exchanger both operated by the calorimeter controller provide precise jacket temperature control. Q mc Delta T.
All data Tsonopoulos and Ambrose 1995. Heat capacity of calorimeter C183JC Increase in temperature of calorimeter question_answer Q. Identify what is releasing heat and what is gaining heat for a given calorimetry experiment.
The below-mentioned formula can be used to calculate specific heat capacity values. Specific Heat Capacity c Specific heat capacity of any substance is defined as the amount of heat required to change the temperature of a unit mass of the substance by 1 degree. This is the amount of heat required to raise 1 gram of that substance by 1C.
Assume that because all of the solutions are dilute aqueous solutions the specific heat capacity of each solution and hence the specific heat capacity of the final solution C g is the same as water which we will assume is 418 J g-1 C-1 C g 418 J g-1 C-1. Total mass of the solution specific heat of the solution change in temperature of the solution. If you have a specific heat capacity in Jg C then you need the mass of the substance in grams.
Place one litre 1 kg of water in the calorimeter. If you have it in Jkg C then you need the mass of the substance in kilograms. Heat sink has the enough heat capacity compared to the sample.
A bomb calorimeter works in the same manner as a coffee cup calorimeter with one big difference. Ii specific heat capacity C g of the solution. Such measurements can be made easily with this.
The entropy and the free energy of formation J. Calculate the heat gained or released by a solution q solution involved in a given calorimetry experiment. List of thermal conductivities Note that the especially high molar values as for paraffin gasoline water and ammonia result from calculating specific heats in terms of moles of molecules.
In the early modern period heat was thought to be a measurement of an invisible fluid known as the caloricBodies were capable of holding a certain amount of this fluid leading to the term heat capacity named and first investigated by Scottish chemist Joseph Black in the 1750s. The definition of the calorie is based on the specific heat of water defined. Unlike differential scanning calorimeters adiabatic flow.
This will require 2669 kJ of heat energy. The vessel is filled with water and the fuel is burned leading to the heating of the water. It should now be becoming clear how convenient this specific heat capacity test is because the only thing to do once the experiment is on the.
DSC 3 - Differential Scanning Calorimeter. Thus the temperature difference between the sample and the. Q m c T.
We would like to show you a description here but the site wont allow us. An alternative truly measuring at operational conditions lies in using an adiabatic flow calorimeter and thus evaluating the enthalpy balance of a small quantity of the HTF in a bypass of the system 5. The mass of the material m The temperature change that occurs DeltaT The specific heat capacity of the material c which you can look up.
A 435-g sample of copper at 999 C is dropped into a beaker containing 156 g of water at 187 C. A simple calorimeter just consists of a thermometer attached to a. The SI unit of specific.
It is usually expressed as calories per degree in terms of the actual amount of material being considered most commonly a mole the molecular weight in grams. Read more See less. In the previous article we discussed the specific heat capacity of substances.
Place the immersion heater into the central hole at the top of the calorimeter. The specific heat also called specific heat capacity is the measure of the heat energy that a substance in a unit quality absorbs or releases when the. If initially the temperature of the water is 200C and after burning the nuts in the calorimeter we measure a water temperature of 333C then the change in temperature of the water T f - T i equals 133C and the heat captured by the calorimeter Q water is 150 g 0001 Calg C 133C or 20 Cal.
The heat capacity in calories per gram is called specific heat.

50 Calorimetry Worksheet Answer Key Chessmuseum Template Library Worksheets Capacity Worksheets Letter Reversals

Pin By Redacted On Chemistry Education Chemistry Education What Is Science Ap Chem
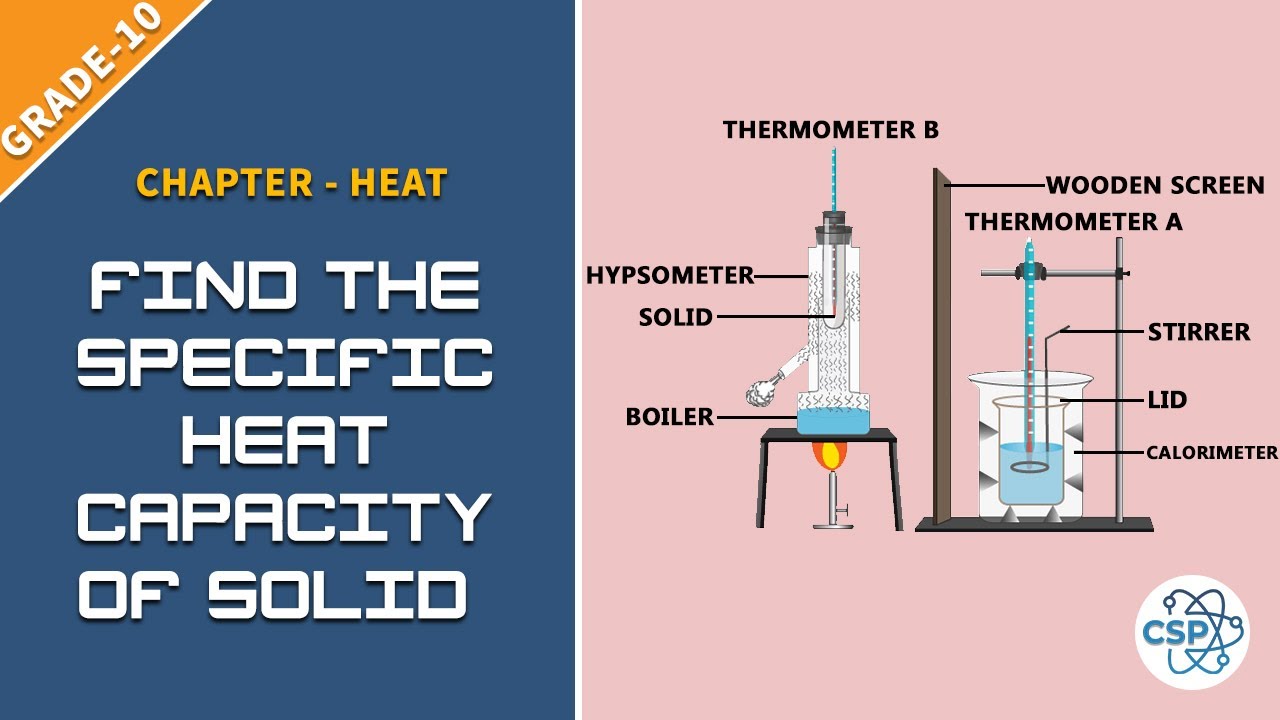
To Find The Specific Heat Capacity Of Solid By Using Method Of Mixtures See Class 10 Physical Properties Heat Science Experiments

Constant Volume Calorimetry For More Precise Work Than The Coffee Cup Calorimeter The Heat Capacity Of The Coffee Cups Chemistry Education Chemical Reactions
0 Response to "Heat Capacity of Calorimeter"
Post a Comment